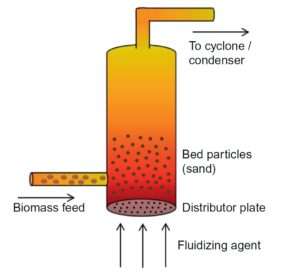
1 solids properties and their effect on the quality of fluidization. The pyrolysis occurs by introducing biomass and steam to a hot fluidized bed of inert material such as coarse sand.
Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor Chemical Engineering World
The dual fluidized bed reactor is a recirculating system in which one half of the unit operates as a steam pyrolysis device for biomass.

. Syngas is produced during the pyrolysis and exits the top of the reactor with the steam. Reactants are pumped into the reactor through a distributor continuously causing the bed to become fluidized. Two dimensional bed of 1m height and 028 width is taken.
Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor 4. The bed of this reactor was sand particles of average size 1800 μm weighed 06 N and the fluidizing fluidwas air. Abstract A fluidized-bed reactor was designed and constructed for practical demonstration of the fluidization of solid particles at different fluid flow rates.
A jet region around a single centrally arranged injector lance in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor is characterized by different parameters like. The most disadvantage with fluidized-bed reactors is that they require fairly little particles 23 mm to reduce heatmass transfer effects. DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION OF A FLUIDIZED BED by Robert Ryan Mota Bachelor of Science California State Polytechnic University Pomona 2010 A Thesis.
The yields from the larger units were found to be disastrously less than those obtained in the pilot plant unit. Bubbling Fluidization This type of fluidization has been called aggregative fluidization and under these conditions the bed appears to be divided into two phases the bubble phase and the emulsion phase. Fluidized beds typically are more complex to design build and operate than other types of reactors such as packed-bed and stirred-tank reactors.
A laboratory scale fluidized bed reactor was designed and fabricated successfully. Numerical study of the hydrodynamics of a freely bubbling fluidized bed is studied here. The bubbles appear to be very similar to gas bubbles formed in.
As the bubbles rise mass transfer of the reactant gases takes place as they flow diffuse in and out of the. Eventually if the gas velocity is increased continuously it will eventually become sufficiently rapid to carry the solid particles upward out of the bed. Before the reactor is started the catalyst pellets lie on a grate at the bottom of the reactor.
This is known as Packed Bed. The disadvantages of fluidized beds are summarized below. Principle Fluid Passes through Bottom with low velocity first to settle down the Solid Material on the Porous Plate called Distributor.
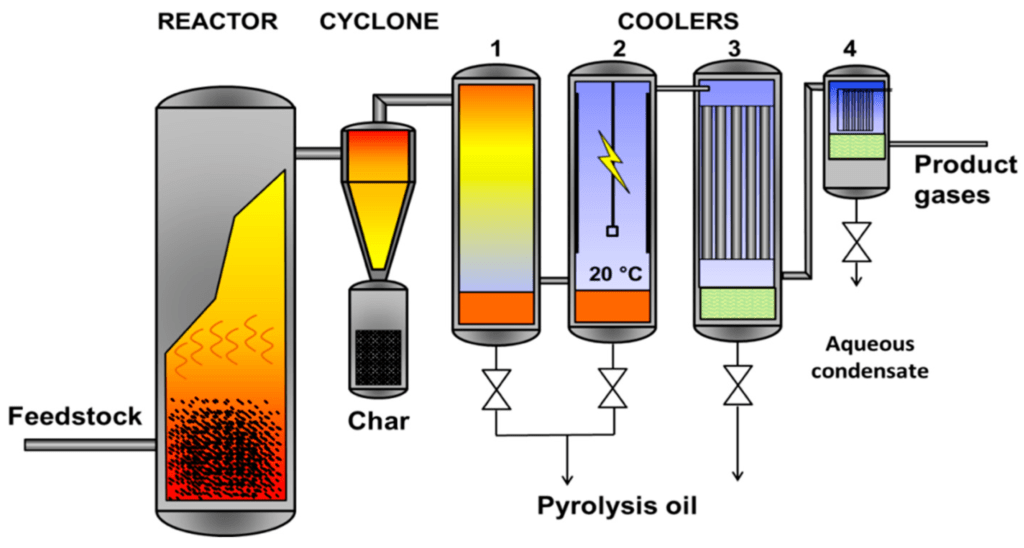
3 particle recovery by means of cyclones. Widespread application of bubbling fluidised bed reactors to chemical processes has been hindered by some inherent drawbacks like the. This paper describes a pilot plant scale circulating fluidized bed unit recently designed constructed and put into operation in the Pulp and Paper Centre at the.
Air was used as the fluidizing medium and sand of. Modeling the Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor BFB. New bubbling fluidized bed with vertically aligned vertical nozzles the fluid dynamics of the fluidized beds have to be determined and analysed especially the flow around the gas nozzles.
At velocities beyond this region the particles are well apart and the. The reactor consists of three sections. Scaleup of fluidized beds can be difficult 1.
Bubbling fluidized beds are composed by a grid air-distribution at the bottom of the reactor to allow a good uniformity of the oxidant agent in the biomass particles avoiding thermal gradients along the radius of the reactor. Fluidized beds are prone to erosion and particle attrition caused. A bed section b freeboard section and c conical closure section with inlet cone.
Syngas is produced during the pyrolysis and exits the top of the reactor with the steam. This paper presents the experimental results on the performance of a PolyethyleneiminePEIsilica adsorbent in capturing CO 2 from ambient air in a laboratory-scale Bubbling Fluidized Bed BFB reactor system. Part A gives general guidelines for the design of large commercial fluidized bed reactors with respect to the following aspects.
Alternatively the fluidizing fluid can be substituted for any given. In Brownsville Texas in 1950 two large 5-m-diameter bubbling fluidized bed FischerTropsch reactors were built based on the results from a 03-m-diameter pilot plant operated with a Group B iron catalyst. The dual fluidized bed reactor is a recirculating system in which one half of the unit operates as a steam pyrolysis device for biomass.
The beds behavior after initial fluidization depends on the state of the reactant. 4 heat transfer tubes. Bubbling beds of fine particles are difficult to predict and are less efficient Rapid mixing of solids causes non-uniform residence times for continuous flow reactors Particle comminuting breakup is common Pipe and vessel walls erode due to collisions by particles.
Circulating fluidized bed reactor design and operation 39 --favourable turndown typically 41 and good load following capabilities. The Fluidized Bed reactor design should be made according to information available in the literature. Equipment Design The movie below shows the operation of a fluidized bed reactor.
The formulas for the design parameters are to be selected from vast literature available on researches in fluidized bed reactors and the study of fluidization profiles. 1 19 Pb H mf Nyakuma et al. This leads to costly needs for grinding lignocellulosic biomass.
5 solids circulation systems. 2 bubble size control through small solid particle size or baffles. The bubbling fluidized bed is doubtless the foremost standard reactor for quick shift.
In this model the reactant gas enters the bottom of the bed and flows up the reactor in the form of bubbles. Octave Levenspiel Emeritus Professor Oregon State University During the Second World War the US had an urgent need to produce enormous quantities of aviation gasoline. The pyrolysis of biomass starts in the bed reactor thanks to the high thermal exchange with the oxidant agent.
Jurnal Teknologi Sciences Engineering 58 2012 8588 In the design of bubbling fluidized beds the distributor 110 pressure drop ΔPd is maintained within a range of 15 to 30 of 100 the bed pressure drop ΔPb 312. A typical fluidized bed reactor. The design parameters which affect the.
The pyrolysis occurs by introducing biomass and steam to a hot fluidized bed of inert material such as coarse sand. When this begins to happen the bubbling and agitation of the solids are still present and this is known as the region of fast fluidization and the bed is a fast-fluidized bed. Types Of reactor 1Bubbling Fluidized Bed 2Circulating Fluidized Bed 3Flash Reactor 4Annular Fluidized Bed 3.
We are going to use the Kunii-Levenspiel bubbling bed model to describe reactions in fluidized beds. Fluid passes through the voids of the solid material. As the process design for efficient airadsorbent contact the regeneration strategy material durability and cyclic regenerability.
Fine particle fluidization the FCC process was proposed was chosen commercial plants were built.

Schematic Diagram Of A Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor Download Scientific Diagram

Characteristics Of Fluidized Bed Reactor Download Scientific Diagram

Bubbling Fluidized Bed An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fluidized Bed Reactor Wikipedia

Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor With An Electrostatic Precipitator Download Scientific Diagram

Bubbling Fluidized Bed Reactor 76 Download Scientific Diagram

Process Schematic For Bubbling Fluidized Bed Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments
Post a Comment